VibroMap: Understanding the Spacing of Vibrotactile Actuators Across the Body
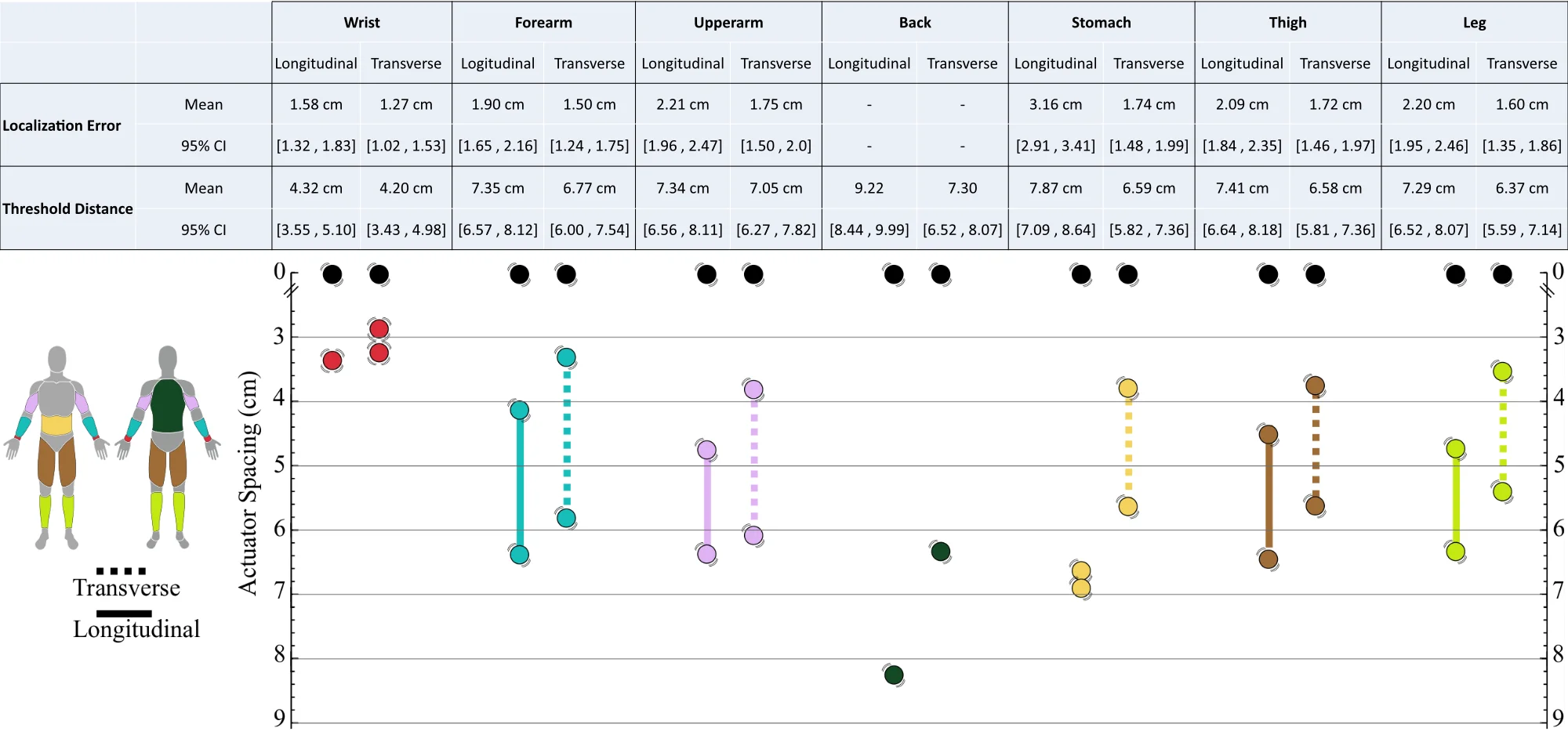
In spite of the great potential of on-body vibrotactile displays for a variety of applications, research lacks an understanding of the spacing between vibrotactile actuators. Through two experiments, we systematically investigate vibrotactile perception on the wrist, forearm, upper arm, back, torso, thigh, and leg, each in transverse and longitudinal body orientation. In the first experiment, we address the maximum distance between vibration motors that still preserves the ability to generate phantom sensations. In the second experiment, we investigate the perceptual accuracy of localizing vibrations in order to establish the minimum distance between vibration motors. Based on the results, we derive VibroMap, a spatial map of the functional range of inter-motor distances across the body. VibroMap supports hardware and interaction designers with design guidelines for constructing body-worn vibrotactile displays.